개요
- K means clustering을 빅쿼리 ML(BQML)을 사용하여 고객을 세분화 하기
- GA360의 데이터를 빅쿼리에 적재해 ML학습하기
- 파이썬을 사용하여 빅쿼리와 연동하고 관련 그래프 시각화하기
목표
- 구글 브랜드 상품을 판매하는 실제 이커머스 스토어인 구글 머천다이스 스토어의 난독화된 GA360 12개월(2016년 8월~2017년 8월)의 데이터를 가지고 고객을 분류
환경 구축
GCP와 주피터 노트북을 연결
config파일이 필요(이전포스트 설명)
PIP install packages and dependencies
1
2
3
4
5
6!pip install google-cloud-bigquery
!pip install google-cloud-bigquery-storage
!pip install pandas-gbq
# Reservation package needed to setup flex slots for flat-rate pricing
!pip install google-cloud-bigquery-reservation1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30Requirement already satisfied: google-cloud-bigquery in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (3.6.0)
Requirement already satisfied: google-cloud-core<3.0.0dev,>=1.6.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (2.3.2)
Requirement already satisfied: requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.21.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (2.28.2)
Requirement already satisfied: protobuf!=3.20.0,!=3.20.1,!=4.21.0,!=4.21.1,!=4.21.2,!=4.21.3,!=4.21.4,!=4.21.5,<5.0.0dev,>=3.19.5 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (4.22.1)
Requirement already satisfied: grpcio<2.0dev,>=1.47.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (1.51.3)
Requirement already satisfied: google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (2.11.0)
Requirement already satisfied: google-resumable-media<3.0dev,>=0.6.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (2.4.1)
Requirement already satisfied: packaging>=20.0.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (23.0)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil<3.0dev,>=2.7.2 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (2.8.2)
Requirement already satisfied: proto-plus<2.0.0dev,>=1.15.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery) (1.22.2)
Requirement already satisfied: google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (2.16.1)
Requirement already satisfied: googleapis-common-protos<2.0dev,>=1.56.2 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (1.58.0)
Requirement already satisfied: grpcio-status<2.0dev,>=1.33.2 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (1.51.3)
Requirement already satisfied: google-crc32c<2.0dev,>=1.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-resumable-media<3.0dev,>=0.6.0->google-cloud-bigquery) (1.5.0)
Requirement already satisfied: six>=1.5 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from python-dateutil<3.0dev,>=2.7.2->google-cloud-bigquery) (1.16.0)
Requirement already satisfied: idna<4,>=2.5 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.21.0->google-cloud-bigquery) (3.4)
Requirement already satisfied: charset-normalizer<4,>=2 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.21.0->google-cloud-bigquery) (3.0.1)
Requirement already satisfied: urllib3<1.27,>=1.21.1 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.21.0->google-cloud-bigquery) (1.26.14)
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.21.0->google-cloud-bigquery) (2022.12.7)
Requirement already satisfied: pyasn1-modules>=0.2.1 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (0.2.8)
Requirement already satisfied: rsa<5,>=3.1.4 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (4.9)
Requirement already satisfied: cachetools<6.0,>=2.0.0 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (5.3.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pyasn1<0.5.0,>=0.4.6 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from pyasn1-modules>=0.2.1->google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.0,<3.0.0dev,>=1.31.5->google-cloud-bigquery) (0.4.8)
Requirement already satisfied: google-cloud-bigquery-storage in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (2.19.0)
Requirement already satisfied: protobuf!=3.20.0,!=3.20.1,!=4.21.0,!=4.21.1,!=4.21.2,!=4.21.3,!=4.21.4,!=4.21.5,<5.0.0dev,>=3.19.5 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from google-cloud-bigquery-storage) (4.22.1)
...
Requirement already satisfied: certifi>=2017.4.17 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from requests<3.0.0dev,>=2.18.0->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.10.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.*,!=2.4.*,!=2.5.*,!=2.6.*,!=2.7.*,!=2.8.*,!=2.9.*,<3.0.0dev,>=1.34.0->google-cloud-bigquery-reservation) (2022.12.7)
Requirement already satisfied: pyasn1<0.5.0,>=0.4.6 in /opt/homebrew/lib/python3.10/site-packages (from pyasn1-modules>=0.2.1->google-auth<3.0dev,>=2.14.1->google-api-core[grpc]!=2.0.*,!=2.1.*,!=2.10.*,!=2.2.*,!=2.3.*,!=2.4.*,!=2.5.*,!=2.6.*,!=2.7.*,!=2.8.*,!=2.9.*,<3.0.0dev,>=1.34.0->google-cloud-bigquery-reservation) (0.4.8)
Installing collected packages: google-cloud-bigquery-reservation
Successfully installed google-cloud-bigquery-reservation-1.10.0설치 후 커널 다시 시작
1
2
3
4# Automatically restart kernel after installs
import IPython
app = IPython.Application.instance()
app.kernel.do_shutdown(True)
Project ID와 인증
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8PROJECT_ID = "your-project-id"
REGION = 'US'
DATA_SET_ID = 'bqml_kmeans' # Ensure you first create a data set in BigQuery
# If you have not built the Data Set, the following command will build it for you
!bq mk --location=$REGION --dataset $PROJECT_ID:$DATA_SET_ID
!gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
Import libraries and define constants
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20import glob
from google.cloud import bigquery
from google.oauth2 import service_account
from google.cloud import bigquery
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import pandas_gbq
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 서비스 계정 키 JSON 파일 경로
key_path = glob.glob("./config/*.json")[0]
# Credentials 객체 생성
credentials = service_account.Credentials.from_service_account_file(key_path)
project_id="your-project-id"
# GCP 클라이언트 객체 생성
pd.set_option('display.float_format', lambda x: '%.3f' % x) # used to display float format
client = bigquery.Client(credentials = credentials,
project = credentials.project_id)
데이터
모델을 구축하기 전에 일반적으로 모델링을 위해 의미 있는 방식으로 데이터 집합을 정리, 탐색 및 집계하는 데 상당한 시간을 투자해야 함. 이 포스트 목적상 이 단계는 BigQuery ML에서 k-평균을 사용한 클러스터링을 우선적으로 보여주기 위해 표시하지 않음.
GA360, GA4차이
- GA360
- GA의 유료 버전으로 무료 버전과 가장 큰 차이점은 ‘데이터 소유권’
- 데이터 소유권이 구글인 무료 버전에 비해 GA360은 데이터 소유권이 사용자
- 때문에 데이터 샘플링이 없고 빅쿼리를 통해 Raw Data를 이용할 수 있음.
- 다만 유료인만큼 연간 1.5억의 사용료를 지불해야 함.
- GA4
- 2019년에 새로 생긴 구글 애널리틱스로 WEB과 APP을 심리스하게 보기 위한 GA
- 360처럼 유료 버전을 쓰지 않아도 빅쿼리로 데이터를 보내주기 때문에 Raw Data를 쿼리 비용만 내고 사용할수 있음.
- GA4 UI에선 속도가 매우 빠르지만 GAUI에 비해 GA4 UI에서는 많은 것으르 보옂쥐 않고 데이터 분석을 위해 제대로 사용하기 위해서는 빅쿼리에 익숙애햐 함.
합성 데이터 구축
최종 목표는 온라인(GA360) 및 오프라인(CRM) 데이터를 모두 사용하는 것.
자체 CRM 데이터를 사용할 수도 있지만, 이 경우에는 보여줄 CRM 데이터가 없으므로 대신 합성 데이터를 생성: 예상 가구 소득(House Hold income, hhi)과 성별
이를 위해 전체 방문자 ID를 해시하고 해시의 마지막 숫자를 기반으로 간단한 규칙을 구축합니다.
- hash: 임의의 길이를 갖는 임의의 데이터를 고정된 길이의 데이터로 매핑하는 것
자체 데이터로 이 프로세스를 실행하면 여러 차원으로 CRM 데이터를 조인할 수 있음.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60# We start with GA360 data, and will eventually build synthetic CRM as an example.
# This block is the first step, just working with GA360
ga360_only_view = 'GA360_View'
shared_dataset_ref = client.dataset(DATA_SET_ID)
ga360_view_ref = shared_dataset_ref.table(ga360_only_view)
ga360_view = bigquery.Table(ga360_view_ref)
ga360_query = '''
SELECT
fullVisitorID,
ABS(farm_fingerprint(fullVisitorID)) AS Hashed_fullVisitorID, # This will be used to generate random data.
MAX(device.operatingSystem) AS OS, # We can aggregate this because an OS is tied to a fullVisitorID.
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Apparel' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS Apparel,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Office' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS Office,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Electronics' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS Electronics,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Limited Supply' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS LimitedSupply,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Accessories' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS Accessories,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Shop by Brand' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS ShopByBrand,
SUM (CASE
WHEN REGEXP_EXTRACT (v2ProductCategory,
r'^(?:(?:.*?)Home/)(.*?)/')
= 'Bags' THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS Bags,
ROUND (SUM (productPrice/1000000),2) AS productPrice_USD
FROM
`bigquery-public-data.google_analytics_sample.ga_sessions_*`,
UNNEST(hits) AS hits,
UNNEST(hits.product) AS hits_product
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20160801'
AND '20160831'
AND geoNetwork.country = 'United States'
AND type = 'EVENT'
GROUP BY
1,
2
'''
ga360_view.view_query = ga360_query.format(PROJECT_ID)
ga360_view = client.create_table(ga360_view) # API request
print(f"Successfully created view at {ga360_view.full_table_id}")
데이터 확인
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14# Show a sample of GA360 data
ga360_query_df = f'''
SELECT * FROM {ga360_view.full_table_id.replace(":", ".")} LIMIT 5
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query
query_job = client.query(ga360_query_df, job_config=job_config) #API Request
df_ga360 = query_job.result()
df_ga360 = df_ga360.to_dataframe()
df_ga360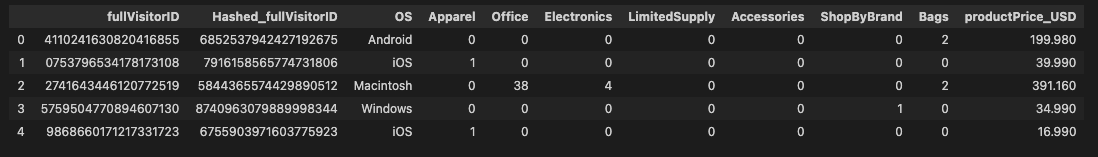
CRM data 추출하여 합성데이터 만들기
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48# Create synthetic CRM data in SQL
CRM_only_view = 'CRM_View'
shared_dataset_ref = client.dataset(DATA_SET_ID)
CRM_view_ref = shared_dataset_ref.table(CRM_only_view)
CRM_view = bigquery.Table(CRM_view_ref)
# Query below works by hashing the fullVisitorID, which creates a random distribution.
# We use modulo to artificially split gender and hhi distribution.
CRM_query = '''
SELECT
fullVisitorID,
IF
(MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,2) = 0,
"M",
"F") AS gender,
CASE
WHEN MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,10) = 0 THEN 55000
WHEN MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,10) < 3 THEN 65000
WHEN MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,10) < 7 THEN 75000
WHEN MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,10) < 9 THEN 85000
WHEN MOD(Hashed_fullVisitorID,10) = 9 THEN 95000
ELSE
Hashed_fullVisitorID
END
AS hhi
FROM (
SELECT
fullVisitorID,
ABS(farm_fingerprint(fullVisitorID)) AS Hashed_fullVisitorID,
FROM
`bigquery-public-data.google_analytics_sample.ga_sessions_*`,
UNNEST(hits) AS hits,
UNNEST(hits.product) AS hits_product
WHERE
_TABLE_SUFFIX BETWEEN '20160801'
AND '20160831'
AND geoNetwork.country = 'United States'
AND type = 'EVENT'
GROUP BY
1,
2)
'''
CRM_view.view_query = CRM_query.format(PROJECT_ID)
CRM_view = client.create_table(CRM_view) # API request
print(f"Successfully created view at {CRM_view.full_table_id}")
데이터 확인
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14# See an output of the synthetic CRM data
CRM_query_df = f'''
SELECT * FROM {CRM_view.full_table_id.replace(":", ".")} LIMIT 5
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query
query_job = client.query(CRM_query_df, job_config=job_config) #API Request
df_CRM = query_job.result()
df_CRM = df_CRM.to_dataframe()
df_CRM
클러스터링을 위한 학습 데이터로 사용할 최종뷰 작성
1 | # Build a final view, which joins GA360 data with CRM data |
데이터 시각화
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14# Show final data used prior to modeling
sql_demo = f'''
SELECT * FROM {final_view.full_table_id.replace(":", ".")} LIMIT 5
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query
query_job = client.query(sql_demo, job_config=job_config) #API Request
df_demo = query_job.result()
df_demo = df_demo.to_dataframe()
df_demo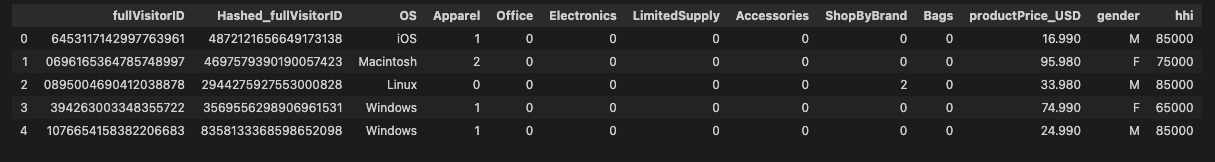
K-Means Model
초기 모델 만들기
- 초기 k-means model을 구축
- 아직 최적의 k 또는 다른 하이퍼 파라미터에는 초점을 맞추지 않겠습니다.
- 몇 가지 추가 사항
- 클러스터링을 위한 피처로 fullVisitorID가 필요하지 않기 때문에 해당 수준에서 그룹화되어 있더라도 fullVisitorID를 입력에서 제거. 전체 방문자 ID를 피처로 사용해서는 안됨.
- 범주형 피처와 숫자 피처가 모두 존재
- 숫자 피처를 정규화할 필요가 없는데, 이는 BigQuery ML이 자동으로 수행하기 때문
1 | def makeModel (n_Clusters, Model_Name): |

더 나은 모델을 만들기 위한 작업
올바른 k 값을 결정하는 것은 전적으로 사용 사례에 따라 달라짐.
ex) 손으로 쓴 숫자를 사전 처리 → k = 10
비즈니스 이해관계자가 세 개의 서로 다른 마케팅 캠페인만 제공하고자 하고 세 개의 고객 클러스터를 식별해야 하는 경우 → k=3그러나 현업에서 위의 예시처럼 딱 떨어지는 사용 사례는 거의 없기 때문에 보통 k의 범위를 지정하고 그 안에서 결과값이 좋은 k를 선택하기도 함.
k 값을 결정하기 위한 수단으로 엘보우 방법을 수행한후 데이비스-볼딘 점수로 평가함.
DBI가 작을수록 cluster를 자세히 구분했다고 말할수 있음(관련 포스트)
아래에서는 엘보 방법을 모두 수행하고 데이비스-볼딘 점수를 얻기 위한 몇 가지 모델을 생성함.
low_k, high_k: 하이퍼 파라미터, 두 값 사이의 모델을 생성.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13# Define upper and lower bound for k, then build individual models for each.
# After running this loop, look at the UI to see several model objects that exist.
low_k = 3
high_k = 15
model_prefix_name = 'kmeans_clusters_'
lst = list(range (low_k, high_k+1)) #build list to iterate through k values
for k in lst:
model_name = model_prefix_name + str(k)
makeModel(k, model_name)
print(f"Model started: {model_name}")
1
2
3
4
5
6# list all current models
models = client.list_models(DATA_SET_ID) # Make an API request.
print("Listing current models:")
for model in models:
full_model_id = f"{model.dataset_id}.{model.model_id}"
print(full_model_id)
1
2
3
4
5# Remove our sample model from BigQuery, so we only have remaining models from our previous loop
model_id = DATA_SET_ID+"."+model_test_name
client.delete_model(model_id) # Make an API request.
print(f"Deleted model '{model_id}'")
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21# This will create a dataframe with each model name, the Davies Bouldin Index, and Loss.
# It will be used for the elbow method and to help determine optimal K
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['davies_bouldin_index', 'mean_squared_distance'])
models = client.list_models(DATA_SET_ID) # Make an API request.
for model in models:
full_model_id = f"{model.dataset_id}.{model.model_id}"
sql =f'''
SELECT
davies_bouldin_index,
mean_squared_distance
FROM ML.EVALUATE(MODEL `{full_model_id}`)
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query, passing in the extra configuration.
query_job = client.query(sql, job_config=job_config) # Make an API request.
df_temp = query_job.to_dataframe() # Wait for the job to complete.
df_temp['model_name'] = model.model_id
df = pd.concat([df, df_temp], axis=0)아래 코드는 원래 이 노트북에서 만든 명명 규칙을 사용했으며, 두 번째 밑줄 뒤에 k 값이 있다고 가정.
model_prefix_name 변수를 변경한 경우, 이 코드가 깨질 수 있음.
1
2
3
4
5
6# This will modify the dataframe above, produce a new field with 'n_clusters', and will sort for graphing
df['n_clusters'] = df['model_name'].str.split('_').map(lambda x: x[2])
df['n_clusters'] = df['n_clusters'].apply(pd.to_numeric)
df = df.sort_values(by='n_clusters', ascending=True)
df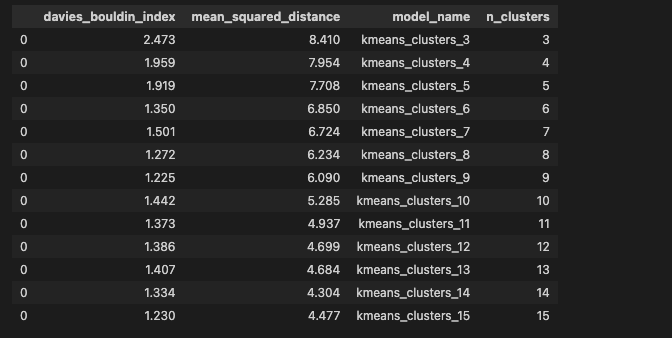
1
df.plot.line(x='n_clusters', y=['davies_bouldin_index', 'mean_squared_distance'])
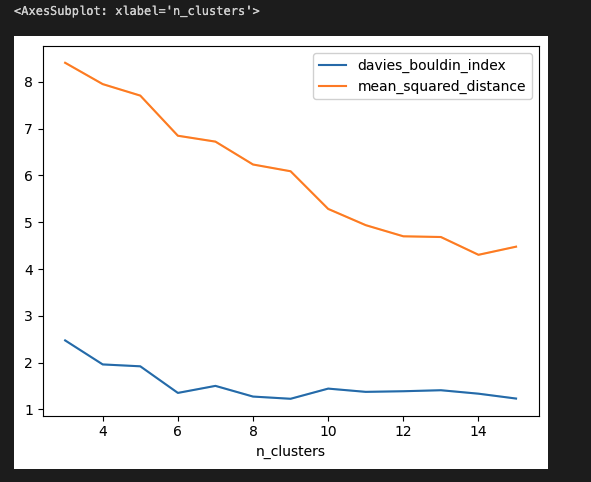
- 참고 - 이 노트북을 실행하면 무작위 클러스터 초기화로 인해 다른 결과를 얻을 수 있음. 도달 범위 실행에 대해 일관되게 동일한 클러스터를 반환하려면 하이퍼파라미터 선택을 통해 초기화를 명시적으로 선택가능.
- k 선택하기: 최적의 k 값을 결정할 때 완벽한 접근 방식이나 프로세스는 정해져 있지 않음. 비즈니스 규칙이나 요구 사항에 따라 결정되는 경우가 많음. 이 예에서는 간단한 요구 사항이 없으므로 다음과 같은 고려 사항을 따를 수도 있음:
- 항상 그런 것은 아니지만, 증분 클러스터가 손실을 크게 줄이지 못하는 자연스러운 ‘엘보 방법’이 있는 경우가 있음. 이 특정 예에서는, 그리고 종종 발견할 수 있듯이, 안타깝게도 자연스러운 ‘엘보’가 존재하지 않으므로 프로세스를 계속 진행해야 함.
- 다음으로 데이비스-볼딘과 k를 차트로 표. 이 점수는 각 클러스터가 얼마나 ‘다른지’를 알려주며, 최적 점수는 0. 클러스터가 5개인 경우 점수는 약 1.4이며, k가 9를 초과하는 경우에만 더 나은 값을 볼 수 있음.
- 마지막으로 각 모델의 차이를 해석하기 시작. 다양한 모델에 대한 평가 모듈을 검토하여 기능의 분포를 이해할 수 있음. 데이터를 통해 성별, 가구 소득, 쇼핑 습관에 따른 패턴을 찾을 수 있음.
최종 클러스터 분석
모델의 특성을 이해하는 데는 두 가지 옵션이 있습니다.
- BigQuery UI를 살펴보거나
- 모델 개체와 프로그래밍 방식
아래에서 후자의 옵션에 대한 간단한 예제를 찾을 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21model_to_use = 'kmeans_clusters_5' # User can edit this
final_model = DATA_SET_ID+'.'+model_to_use
sql_get_attributes = f'''
SELECT
centroid_id,
feature,
categorical_value
FROM
ML.CENTROIDS(MODEL {final_model})
WHERE
feature IN ('OS','gender')
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query
query_job = client.query(sql_get_attributes, job_config=job_config) #API Request
df_attributes = query_job.result()
df_attributes = df_attributes.to_dataframe()
df_attributes.head()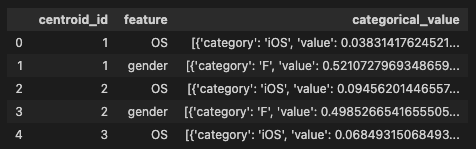
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56# get numerical information about clusters
sql_get_numerical_attributes = f'''
WITH T AS (
SELECT
centroid_id,
ARRAY_AGG(STRUCT(feature AS name,
ROUND(numerical_value,1) AS value)
ORDER BY centroid_id)
AS cluster
FROM ML.CENTROIDS(MODEL {final_model})
GROUP BY centroid_id
),
Users AS(
SELECT
centroid_id,
COUNT(*) AS Total_Users
FROM(
SELECT
* EXCEPT(nearest_centroids_distance)
FROM
ML.PREDICT(MODEL {final_model},
(
SELECT
*
FROM
{final_view.full_table_id.replace(":", ".")}
)))
GROUP BY centroid_id
)
SELECT
centroid_id,
Total_Users,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'Apparel') AS Apparel,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'Office') AS Office,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'Electronics') AS Electronics,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'LimitedSupply') AS LimitedSupply,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'Accessories') AS Accessories,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'ShopByBrand') AS ShopByBrand,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'Bags') AS Bags,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'productPrice_USD') AS productPrice_USD,
(SELECT value from unnest(cluster) WHERE name = 'hhi') AS hhi
FROM T LEFT JOIN Users USING(centroid_id)
ORDER BY centroid_id ASC
'''
job_config = bigquery.QueryJobConfig()
# Start the query
query_job = client.query(sql_get_numerical_attributes, job_config=job_config) #API Request
df_numerical_attributes = query_job.result()
df_numerical_attributes = df_numerical_attributes.to_dataframe()
df_numerical_attributes.head()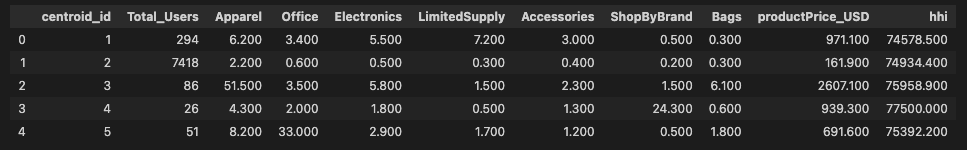
- 위의 결과를 분석해보면 1번 클러스터는 유저수가 두번째로 많고, 제일 유저수가 많은 클러스터 2번보다 구매율이 높은걸 알수 있음
- 2번 클러스터는 가장 인구가 많지만 구매 횟수가 적고 평균 지출액이 적음. 브랜드 충성도가 높다기 보다는 일회성 구매자
- 3번 클러스터는 의류에 관심이 많고 평균 구매 가격이 제일 높음. 브랜드별로 소비하진 않지만 가치가 가장 높은 고객
- 4번 클러스터는 브랜드 별로 소비를 많이 하는 고객들이 몰려 있음.
- 5번 클러스터는 사무용품에 가장 돈을 많이 사용하는 고객
Export to GA360
- 모델을 완성한 후에는 이를 추론에 사용
- 아래 코드는 사용자를 점수화하거나 클러스터에 할당하는 방법을 간략하게 설명
- 이 코드에는 CENTROID_ID라는 레이블이 붙습니다. 이 코드 자체도 도움이 되지만, 이 점수를 다시 GA360으로 수집하는 프로세스를 권장
- BigQuery 테이블에서 Google 애널리틱스 360으로 BigQuery ML 예측을 내보내는 가장 쉬운 방법은 MoDeM(마케팅을 위한 모델 배포) 참조 구현을 사용하는 것
- MoDeM은 Google 광고, 디스플레이 및 동영상 360, 검색 광고 360에서 최종적으로 활성화할 수 있도록 데이터를 Google 애널리틱스에 로드하는 데 도움이 됨
1 | sql_score = f''' |