Course
Neural Networks
- matrix multiplication: it is a binary operation that takes a pair of matrices and produces another matrix. It is defined as the product of an m×n matrix and an n×p matrix, resulting in an m×p matrix. The product is calculated by taking the dot product of the rows of the first matrix with the columns of the second matrix. The entry in the i-th row and j-th column of the resulting matrix is obtained by multiplying each element of the i-th row of the first matrix by the corresponding element of the j-th column of the second matrix and then summing the products.
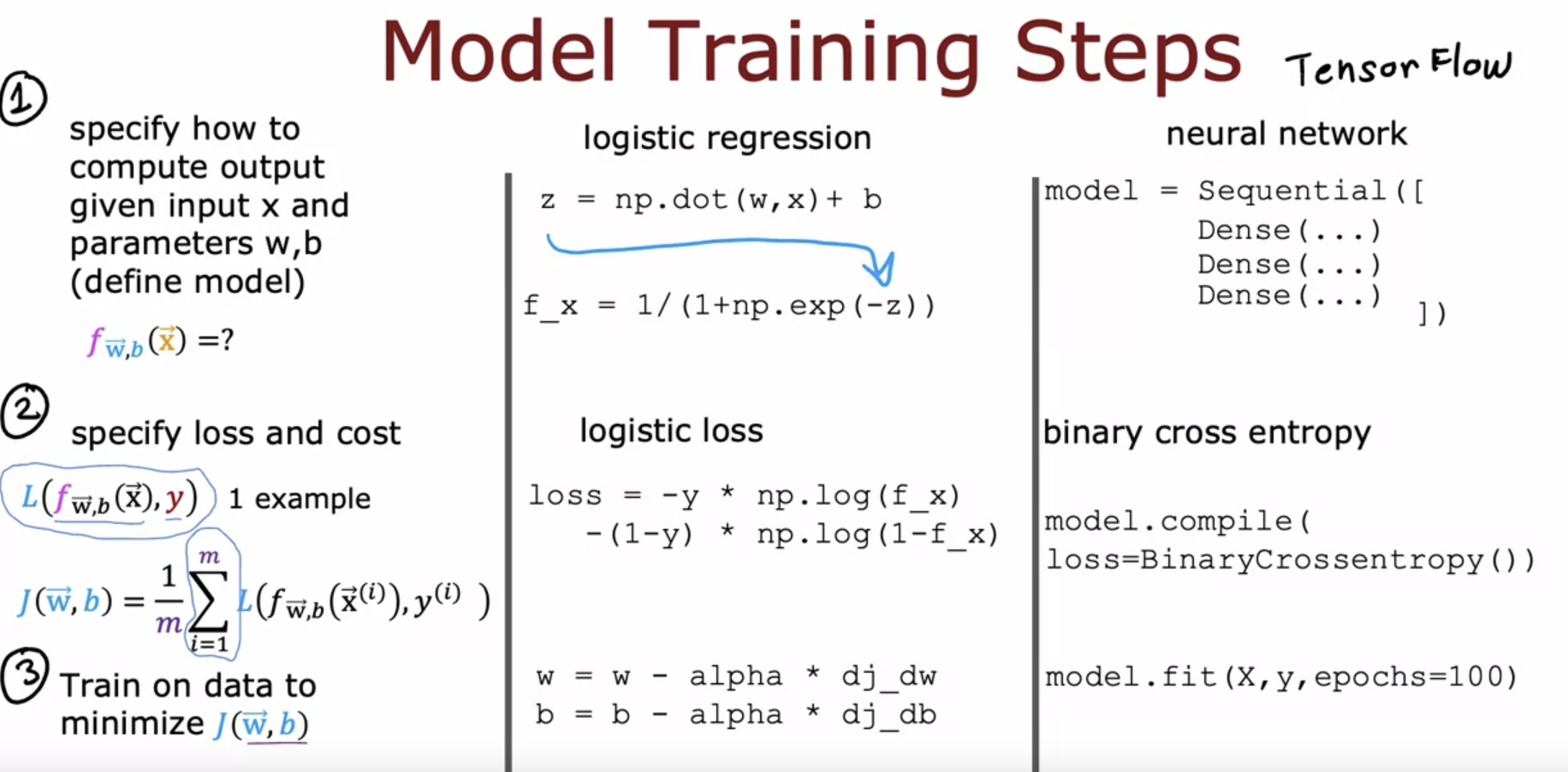
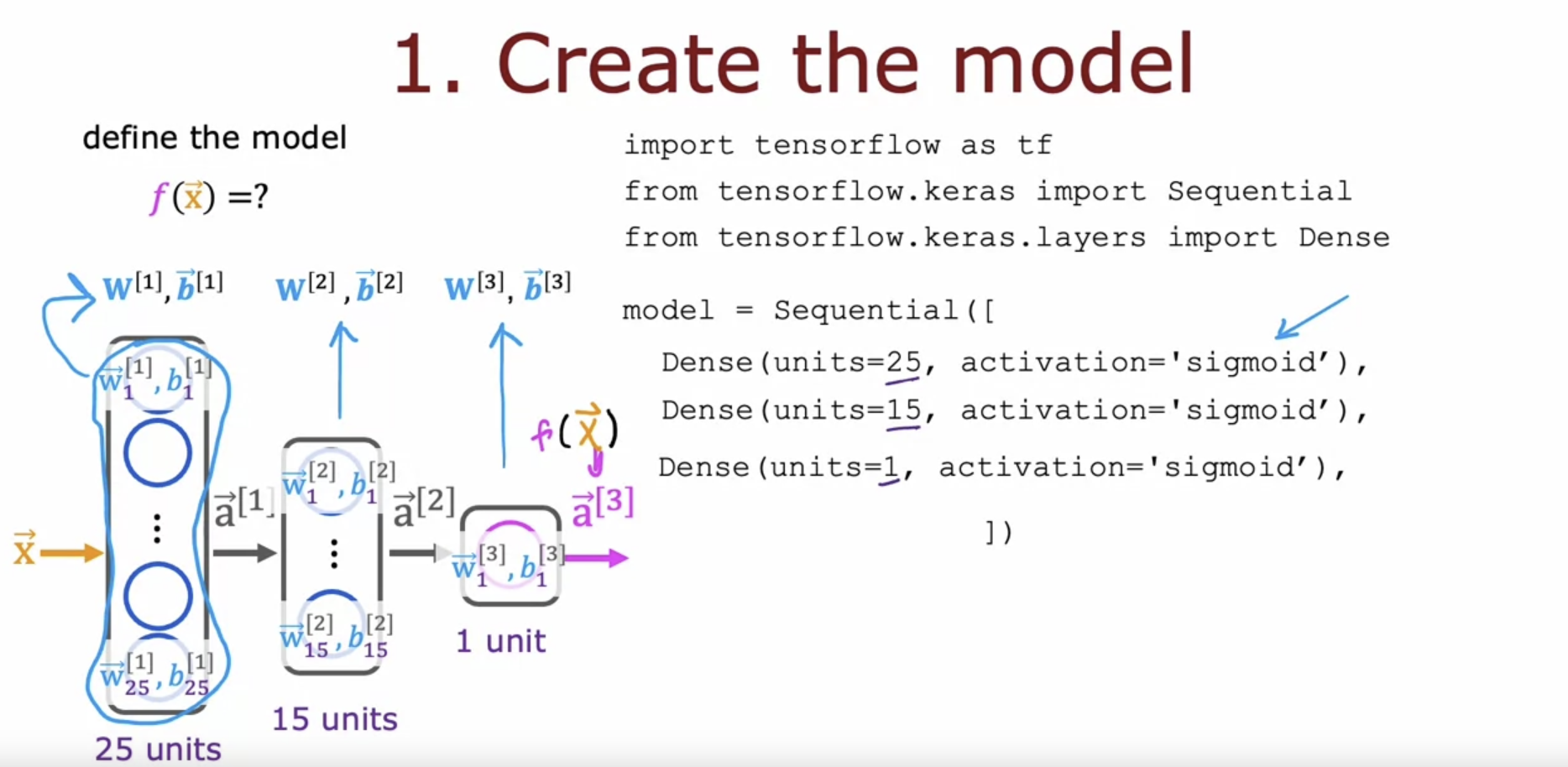
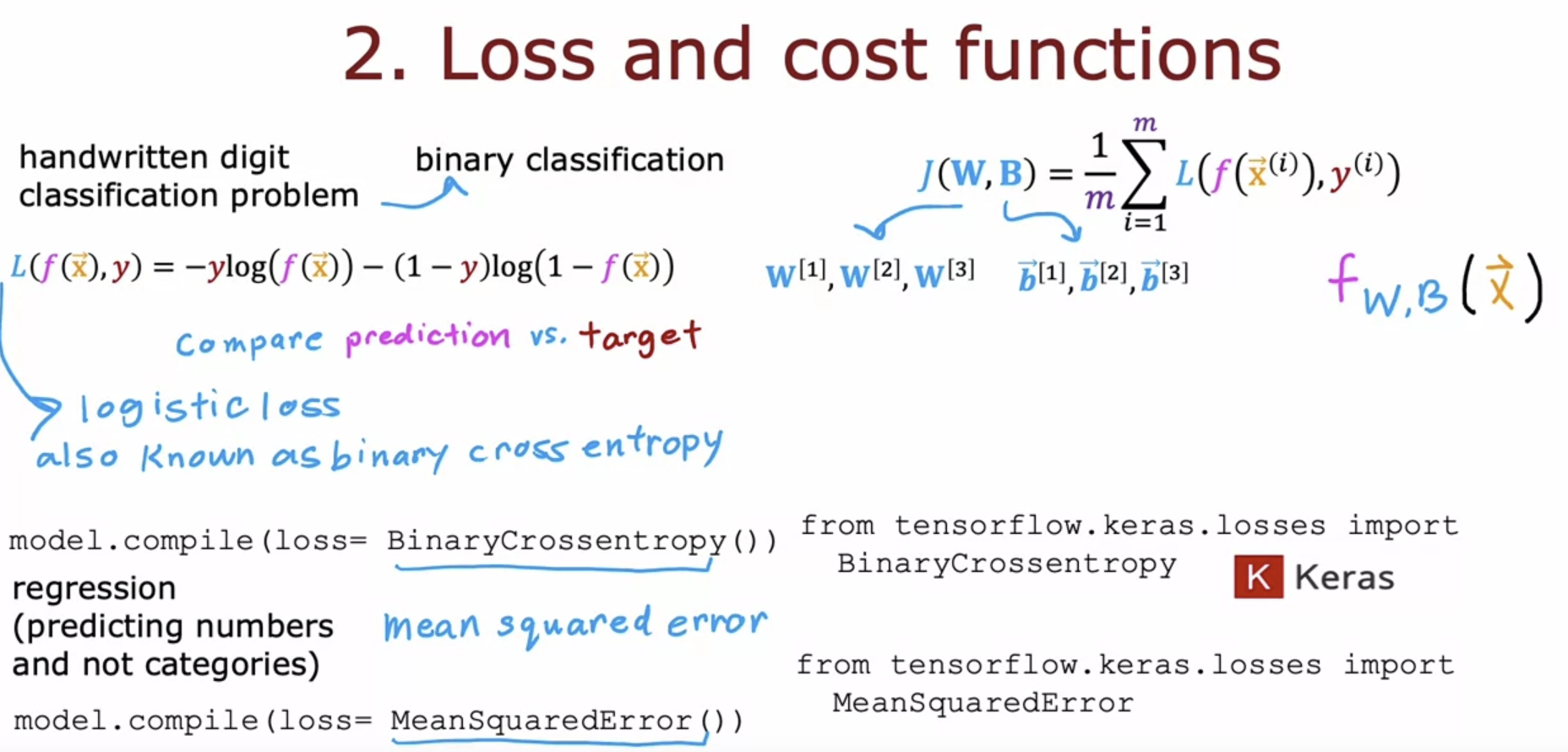
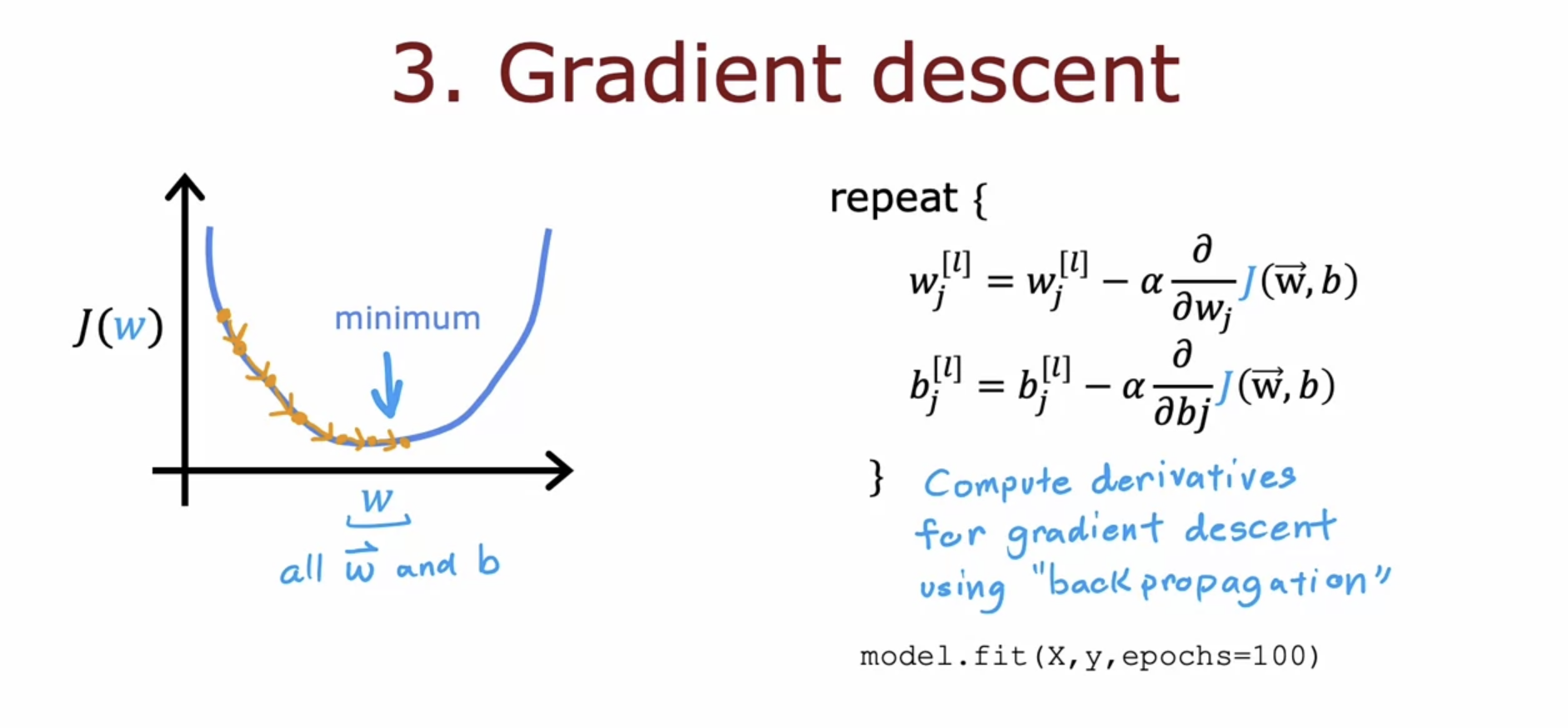
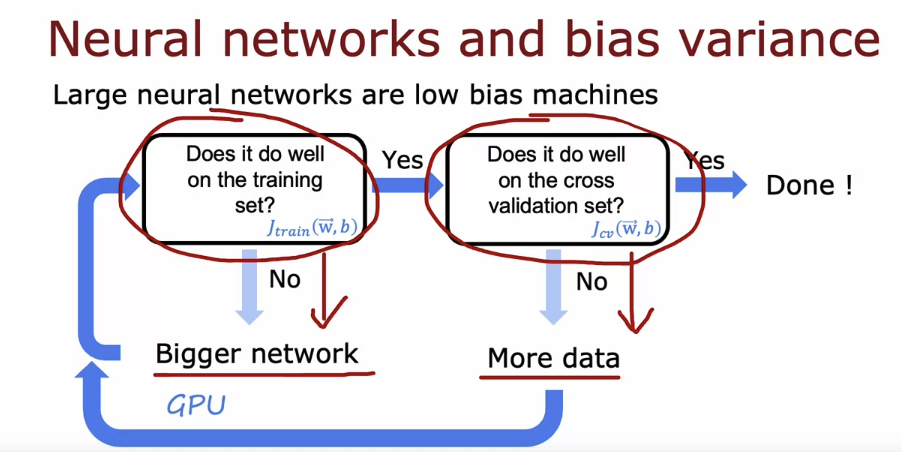
Nueral Network training
ML advice
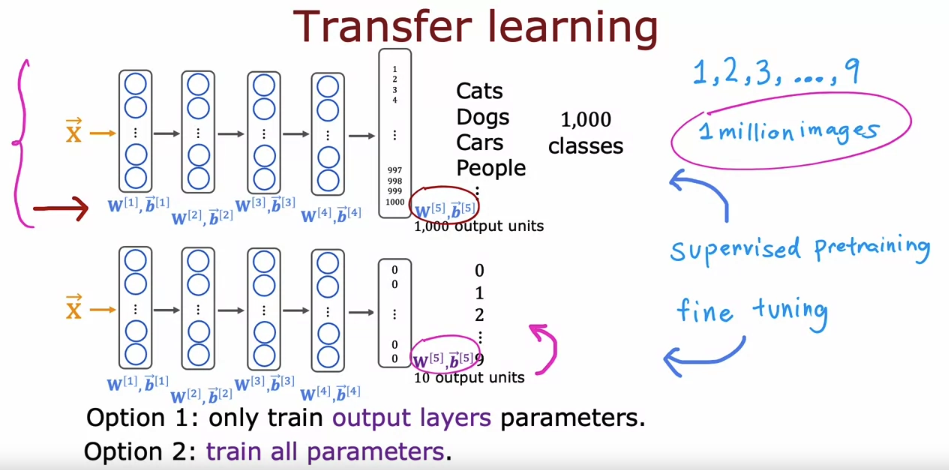
One nice thing about transfer learning as well is maybe you don’t need to be the one to carry out supervised pre-training. For a lot of neural networks, there will already be researchers they have already trained a neural network on a large image and will have posted a trained neural networks on the Internet, freely licensed for anyone to download and use. What that means is rather than carrying out the first step yourself, you can just download the neural network that someone else may have spent weeks training and then replace the output layer with your own output layer and carry out either Option 1 or Option 2 to fine tune a neural network that someone else has already carried out supervised pre-training on, and just do a little bit of fine tuning to quickly be able to get a neural network that performs well on your task. Downloading a pre-trained model that someone else has trained and provided for free is one of those techniques where by building on each other’s work on machine learning community we can all get much better results. By the generosity of other researchers that have pre-trained and posted their neural networks online.
One restriction of pre-training though, is that the image type x has to be the same for the pre-training and fine-tuning steps. If your goal is to build a speech recognition system to process audio, then a neural network pre-trained on images probably won’t do much good on audio. Instead, you want a neural network pre-trained on audio data, there you then fine tune on your own audio dataset and the same for other types of applications. You can pre-train a neural network on text data and If your application has a save feature input x of text data, then you can fine tune that neural network on your own data.

To summarize, these are the two steps for transfer learning. Step 1 is download neural network with parameters that have been pre-trained on a large dataset with the same input type as your application.
Decision Tree

- entropy function
- measure of the impurity of a set of data.
- starts from zero, goes up to one, and then comes back down to zero as a function of the fraction of positive examples in your sample.
- similar with Gini crtiteria
- if there’s a node with a lot of examples in it with high entropy that seems worse than if there was a node with just a few examples in it with high entropy. Because entropy, as a measure of impurity, is worse if you have a very large and impure dataset compared to just a few examples and a branch of the tree that is very impure.
- information gain
- it measures the reduction in entropy that you get in your tree resulting from making a split.
- recursive algorithm
- the way you build a decision tree at the root is by building other smaller decision trees in the left and right sub-branches
- recursion refers to writing code that calls itself.